
40+ Child Care Statistics & Trends in the U.S.
Uncover the latest insights into child care in the US with our 40+ essential statistics, providing a detailed look at the state of child care services, accessibility, and family dynamics.
Modern lifestyle has caused a surge in obesity throughout the world and, coupled with it, the intention for weight loss has also increased. Losing weight requires both willpower and dedication; however, even more important is knowing the right methods and lifestyle changes that must be adopted to achieve permanent changes.
Employers should be invested in the health and wellbeing of their employees, as a healthy employee is more productive, has fewer health issues, and costs the company less in benefits. In this article, we will shed some light on what the science says about losing weight and its importance for employees.
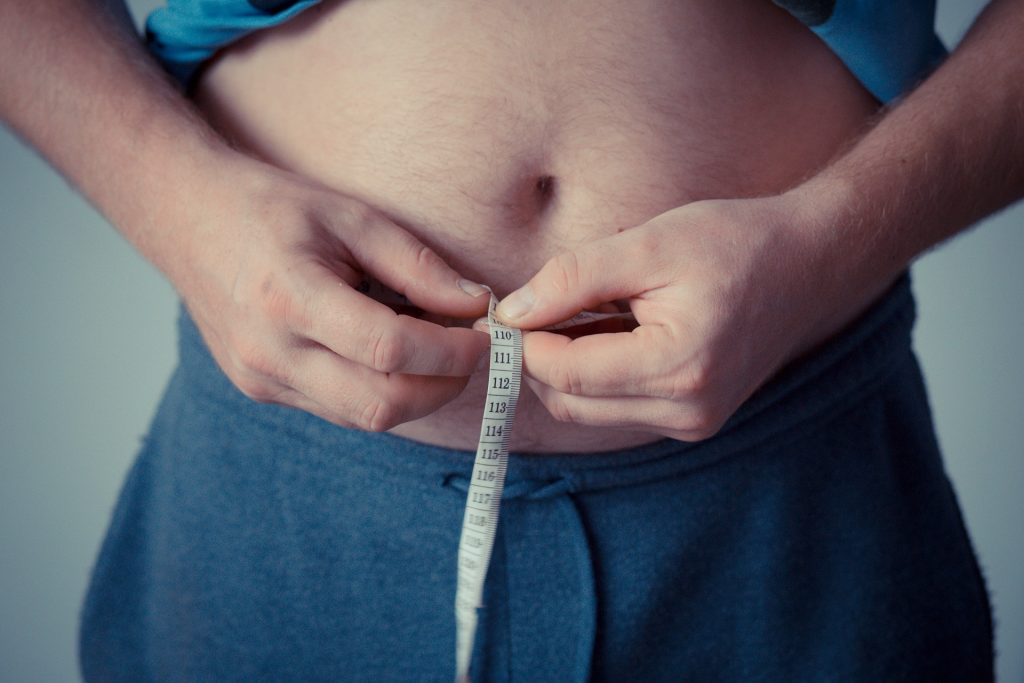



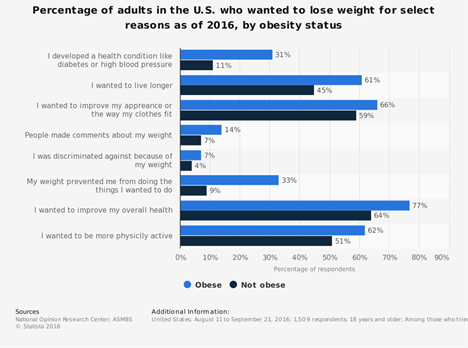
Losing weight is a commitment that many make, yet most have trouble keeping. Gaining knowledge may be the best approach to losing weight. Having a fact-based approach and trusting the science behind it is a safe way to achieve weight loss. Companies can help their employees with weight management programs.
Browse our curated list of vendors to find the best solution for your needs.
Subscribe to our newsletter for the latest trends, expert tips, and workplace insights!

Uncover the latest insights into child care in the US with our 40+ essential statistics, providing a detailed look at the state of child care services, accessibility, and family dynamics.

Can fertility benefits become a recruiting and retention magnet in the ever-evolving workplace landscape?

Diabetes is the most expensive chronic illness in the US. The global health expenditure reached $966 billion, with North America accounting for 42.9% of this, or $415 billion.

Unravel the profound implications of influenza on public health and the economy. Discover the significance of flu vaccinations and workplace measures, shedding light on strategies for a healthier society.
Shortlister Connect is a tool specifically designed to be utilized by the HR and Procurement/Sourcing teams within mid-size, large and jumbo employers. Shortlister Connect allows these teams to efficiently research & identify their optimal vendor partners, track existing vendor relationships & performance and “connect” with other employers to share successes and vendor experiences.
If you are not on the HR or Procurement/Sourcing team within an employer with over 200 employees, you will not be granted access to Connect. Examples of individuals that would not be granted access include, but are not limited to: vendors, students, practitioners, researchers, other non-employers or anyone that is unwilling to identify themselves will not pass our vetting criteria. If you are a consultant, Shortlister offers a specialized product for consultants, called Shortlister Select. You can email Tom Ciccotti at tciccotti@myshortlister.com to learn more about Shortlister Select.
***Shortlister retains the exclusive right to grant or deny access to any party to ensure the privacy of the vendors in our system.
Please login with your LinkedIn Credentials
Used by most of the top employee benefits consultants in the US, Shortlister is where you can find, research and select HR and benefits vendors for your clients.
Shortlister helps you reach your ideal prospects. Claim your free account to control your message and receive employer, consultant and health plan leads.